The Android SDK separates tools, platforms, and other components into packages you can download using the SDK Manager. For example, when the SDK Tools are updated or a new version of the Android platform is released, you can use the SDK Manager to quickly download them to your environment.
You can launch the SDK Manager in one of the following ways:
- From Eclipse (with ADT), select Window > Android SDK Manager.
- From Android Studio, select Tools > Android > SDK Manager.
- On Windows, double-click the
SDK Manager.exefile at the root of the Android SDK directory. - On Mac or Linux, open a terminal and navigate to the
tools/directory in the location where the Android SDK is installed, then executeandroid sdk.
You can select which packages you want to download by toggling the checkboxes on the left, then click Install to install the selected packages.
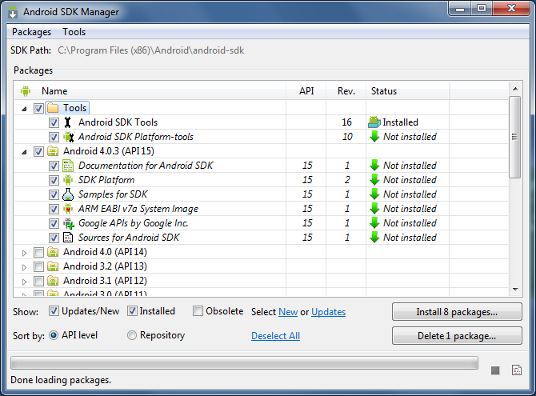
Figure 1. The Android SDK Manager shows the SDK packages that are available, already installed, or for which an update is available.
There are several different packages available for the Android SDK. The table below describes most of the available packages and where they're located in your SDK directory once you download them.
Recommended Packages
Here's an outline of the packages required and those we recommend you use:
- SDK Tools
- Required. Your new SDK installation already has the latest version. Make sure you keep this up to date.
- SDK Platform-tools
- Required. You must install this package when you install the SDK for the first time.
- SDK Platform
- Required.You must download at least one platform into your
environment so you're able to compile your application. In order to provide the best user experience
on the latest devices, we recommend that you use the latest platform version as your build target.
You'll still be able to run your app on older versions, but you must build against the latest
version in order to use new features when running on devices with the latest version of Android.
To get started, download the latest Android version, plus the lowest version you plan to support (we recommend Android 2.2 for your lowest version).
- System Image
- Recommended. Although you might have one or more Android-powered devices on which to test your app, it's unlikely you have a device for every version of Android your app supports. It's a good practice to download system images for all versions of Android your app supports and test your app running on them with the Android emulator.
- Android Support
- Recommended. Includes a static library that allows you to use some of the latest Android APIs (such as fragments, plus others not included in the framework at all) on devices running a platform version as old as Android 1.6. All of the activity templates available when creating a new project with the ADT Plugin require this. For more information, read Support Library.
- SDK Samples
- Recommended. The samples give you source code that you can use to learn about Android, load as a project and run, or reuse in your own app. Note that multiple samples packages are available — one for each Android platform version. When you are choosing a samples package to download, select the one whose API Level matches the API Level of the Android platform that you plan to use.
Tip: For easy access to the SDK tools from a command line, add the
location of the SDK's tools/ and
platform-tools to your PATH environment variable.
The above list is not comprehensive and you can add new sites to download additional packages from third-parties.
In some cases, an SDK package may require a specific minimum revision of another package or SDK tool. The development tools will notify you with warnings if there is dependency that you need to address. The Android SDK Manager also enforces dependencies by requiring that you download any packages that are needed by those you have selected.
Adding New Sites
By default, Available Packages displays packages available from the Android Repository and Third party Add-ons. You can add other sites that host their own Android SDK add-ons, then download the SDK add-ons from those sites.
For example, a mobile carrier or device manufacturer might offer additional API libraries that are supported by their own Android-powered devices. In order to develop using their libraries, you must install their Android SDK add-on, if it's not already available under Third party Add-ons.
If a carrier or device manufacturer has hosted an SDK add-on repository file on their web site, follow these steps to add their site to the Android SDK Manager:
- Select Available Packages in the left panel.
- Click Add Add-on Site and enter the URL of the
repository.xmlfile. Click OK.
Any SDK packages available from the site will now be listed under a new item named User Add-ons.
Troubleshooting
Problems connecting to the SDK repository
If you are using the Android SDK Manager to download packages and are encountering connection problems, try connecting over http, rather than https. To switch the protocol used by the Android SDK Manager, follow these steps:
- With the Android SDK Manager window open, select "Settings" in the left pane.
- On the right, in the "Misc" section, check the checkbox labeled "Force https://... sources to be fetched using http://..."
- Click Save & Apply.