This lesson teaches you to
- Best Practices for Recommendations
- Create a Recommendations Service
- Build Recommendations
- Run Recommendations Service
Try it out
When interacting with TVs, users generally prefer to give minimal input before watching content. An ideal scenario for many TV users is: sit down, turn on, and watch. The fewest steps to get users to content they enjoy is generally the path they prefer.
The Android framework assists with minimum-input interaction by providing a recommendations row on the home screen. Content recommendations appear as the first row of the TV home screen after the first use of the device. Contributing recommendations from your app's content catalog can help bring users back to your app.
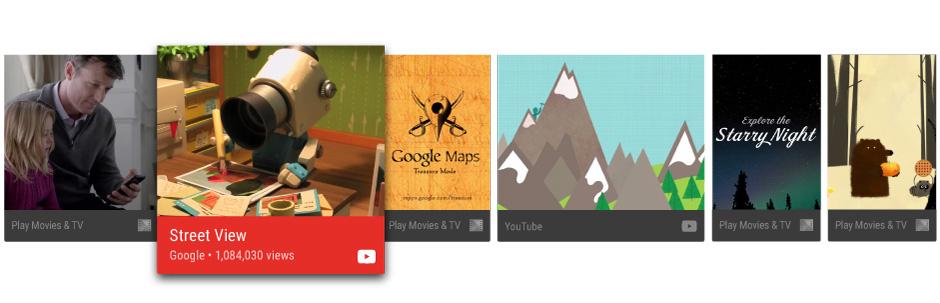
Figure 1. An example of the recommendations row.
This lesson teaches you how to create recommendations and provide them to the Android framework so users can easily discover and enjoy your app content. This discussion describes some code from the Android Leanback sample app.
Best Practices for Recommendations
Recommendations help users quickly find the content and apps they enjoy. Creating recommendations that are high-quality and relevant to users is an important factor in creating a great user experience with your TV app. For this reason, you should carefully consider what recommendations you present to the user and manage them closely.
Types of Recommendations
When you create recommendations, you should link users back to incomplete viewing activities or suggest activities that extend that to related content. Here are some specific type of recommendations you should consider:
- Continuation content recommendations for the next episode for users to resume watching a series.
- New content recommendations, such as for a new first-run episode, if the user finished watching another series.
- Related content recommendations based on the users historic viewing behavior.
For more information on how to design recommendation cards for the best user experience, see Recommendation Row in the Android TV Design Spec.
Refreshing Recommendations
When refreshing recommendations, don't just remove and repost them, because doing so causes the recommendations to appear at the end of the recommendations row. Once a content item, such as a movie, has been played, remove it from the recommendations.
Customizing Recommendations
You can customize recommendation cards to convey branding information, by setting user interface elements such as the card's foreground and background image, color, app icon, title, and subtitle. To learn more, see Recommendation Row in the Android TV Design Spec.
Create a Recommendations Service
Content recommendations are created with background processing. In order for your application to contribute to recommendations, create a service that periodically adds listings from your app's catalog to the system's list of recommendations.
The following code example illustrates how to extend IntentService to
create a recommendation service for your application:
public class UpdateRecommendationsService extends IntentService {
private static final String TAG = "UpdateRecommendationsService";
private static final int MAX_RECOMMENDATIONS = 3;
public UpdateRecommendationsService() {
super("RecommendationService");
}
@Override
protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) {
Log.d(TAG, "Updating recommendation cards");
HashMap<String, List<Movie>> recommendations = VideoProvider.getMovieList();
if (recommendations == null) return;
int count = 0;
try {
RecommendationBuilder builder = new RecommendationBuilder()
.setContext(getApplicationContext())
.setSmallIcon(R.drawable.videos_by_google_icon);
for (Map.Entry<String, List<Movie>> entry : recommendations.entrySet()) {
for (Movie movie : entry.getValue()) {
Log.d(TAG, "Recommendation - " + movie.getTitle());
builder.setBackground(movie.getCardImageUrl())
.setId(count + 1)
.setPriority(MAX_RECOMMENDATIONS - count)
.setTitle(movie.getTitle())
.setDescription(getString(R.string.popular_header))
.setImage(movie.getCardImageUrl())
.setIntent(buildPendingIntent(movie))
.build();
if (++count >= MAX_RECOMMENDATIONS) {
break;
}
}
if (++count >= MAX_RECOMMENDATIONS) {
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Unable to update recommendation", e);
}
}
private PendingIntent buildPendingIntent(Movie movie) {
Intent detailsIntent = new Intent(this, DetailsActivity.class);
detailsIntent.putExtra("Movie", movie);
TaskStackBuilder stackBuilder = TaskStackBuilder.create(this);
stackBuilder.addParentStack(DetailsActivity.class);
stackBuilder.addNextIntent(detailsIntent);
// Ensure a unique PendingIntents, otherwise all
// recommendations end up with the same PendingIntent
detailsIntent.setAction(Long.toString(movie.getId()));
PendingIntent intent = stackBuilder.getPendingIntent(0, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
return intent;
}
}
In order for this service to be recognized by the system and run, register it using your app manifest. The following code snippet illustrates how to declare this class as a service:
<manifest ... >
<application ... >
...
<service
android:name="com.example.android.tvleanback.UpdateRecommendationsService"
android:enabled="true" />
</application>
</manifest>
Build Recommendations
Once your recommendation service starts running, it must create recommendations and pass them to
the Android framework. The framework receives the recommendations as Notification objects that use a specific template and are marked with a specific
category.
Setting the Values
To set the UI element values for the recommendation card, you create a builder class that follows the builder pattern described as follows. First, you set the values of the recommendation card elements.
public class RecommendationBuilder {
...
public RecommendationBuilder setTitle(String title) {
mTitle = title;
return this;
}
public RecommendationBuilder setDescription(String description) {
mDescription = description;
return this;
}
public RecommendationBuilder setImage(String uri) {
mImageUri = uri;
return this;
}
public RecommendationBuilder setBackground(String uri) {
mBackgroundUri = uri;
return this;
}
...
Creating the Notification
Once you've set the values, you then build the notification, assigning the values from the builder
class to the notification, and calling NotificationCompat.Builder.build().
Also, be sure to call
setLocalOnly()
so the NotificationCompat.BigPictureStyle notification won't show up
on other devices.
The following code example demonstrates how to build a recommendation.
public class RecommendationBuilder {
...
public Notification build() throws IOException {
...
Notification notification = new NotificationCompat.BigPictureStyle(
new NotificationCompat.Builder(mContext)
.setContentTitle(mTitle)
.setContentText(mDescription)
.setPriority(mPriority)
.setLocalOnly(true)
.setOngoing(true)
.setColor(mContext.getResources().getColor(R.color.fastlane_background))
.setCategory(Notification.CATEGORY_RECOMMENDATION)
.setLargeIcon(image)
.setSmallIcon(mSmallIcon)
.setContentIntent(mIntent)
.setExtras(extras))
.build();
return notification;
}
}
Run Recommendations Service
Your app's recommendation service must run periodically in order to create current
recommendations. To run your service, create a class that runs a timer and invokes
it at regular intervals. The following code example extends the BroadcastReceiver class to start periodic execution of a recommendation service
every half hour:
public class BootupActivity extends BroadcastReceiver {
private static final String TAG = "BootupActivity";
private static final long INITIAL_DELAY = 5000;
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Log.d(TAG, "BootupActivity initiated");
if (intent.getAction().endsWith(Intent.ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED)) {
scheduleRecommendationUpdate(context);
}
}
private void scheduleRecommendationUpdate(Context context) {
Log.d(TAG, "Scheduling recommendations update");
AlarmManager alarmManager = (AlarmManager) context.getSystemService(Context.ALARM_SERVICE);
Intent recommendationIntent = new Intent(context, UpdateRecommendationsService.class);
PendingIntent alarmIntent = PendingIntent.getService(context, 0, recommendationIntent, 0);
alarmManager.setInexactRepeating(AlarmManager.ELAPSED_REALTIME_WAKEUP,
INITIAL_DELAY,
AlarmManager.INTERVAL_HALF_HOUR,
alarmIntent);
}
}
This implementation of the BroadcastReceiver class must run after start
up of the TV device where it is installed. To accomplish this, register this class in your app
manifest with an intent filter that listens for the completion of the device boot process. The
following sample code demonstrates how to add this configuration to the manifest:
<manifest ... >
<application ... >
<receiver android:name="com.example.android.tvleanback.BootupActivity"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="false">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED"/>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
</manifest>
Important: Receiving a boot completed notification requires that your app
requests the RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED permission.
For more information, see ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED.
In your recommendation service class' onHandleIntent()
method, post the recommendation to the manager as follows:
Notification notification = notificationBuilder.build(); mNotificationManager.notify(id, notification);